Industry Outlook 2025-26: Skilling Initiatives Driving Growth and Transformation in India’s Apparel Sector
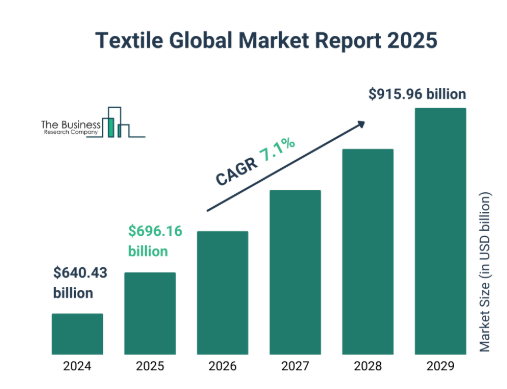
The Indian textile and apparel industry is the second-largest manufacturer globally, with an estimated export value of ~US$ 44.4 billion and a domestic market of ~US$ 75 billion as of 2023-24. The textile market size has grown strongly in recent years. It will further grow from $640.43 billion in 2024 to $696.16 billion in 2025 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.7%. The sector contributes approximately 2.3% to India's GDP and provides direct employment to around 45 million individuals, with an additional 100 million employed indirectly. India remains one of the few countries with an integrated supply chain, spanning natural and synthetic fibers to finished goods manufacturing.
Fresh industry insights indicate that as of 2023, India's textile and apparel sector was valued at approximately ₹10.5 lakh crore and is projected to reach ₹15 lakh crore by 2025. The export market, which stood at ₹3.9 lakh crore in 2023, is expected to grow to ₹5.2 lakh crore by 2025-26. Within this, apparel accounts for nearly 68% of the domestic market, followed by technical textiles (24%) and home textiles (8%). This highlights the critical need for a skilled workforce to sustain industry expansion and global competitiveness.
The global textile and apparel trade has now surpassed US$ 920 billion in 2023 and is expected to cross US$ 1.2 trillion by 2026, driven by rising demand for sustainable fashion, digitalization in manufacturing, and an expanding e-commerce ecosystem.
Technological advancements, sustainability measures, and automation are transforming the sector. AI-driven textile manufacturing, automated fabric cutting, and smart production processes are becoming integral to the industry, emphasizing the need for an up-skilled workforce ready to operate within this evolving landscape.
Current Workforce and Projected Demand
The sector currently employs around 4.5 crore individuals directly and an additional 10 crore in allied sectors. With increasing demand for high-quality and sustainable apparel, the industry is projected to generate employment for an additional 75 lakh workers by 2026. Bridging this workforce gap through skilling initiatives is imperative to ensure workers are equipped with the latest industry-relevant competencies.
Challenges in Workforce Skilling
Despite its strong potential, the apparel sector faces significant skilling challenges. Many workers come from economically weaker backgrounds and lack access to formal training. The increasing adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies has widened the skill gap, with nearly 60% of the workforce requiring reskilling or upskilling.
Furthermore, the informal nature of employment, particularly in decentralized sectors such as small-medium scale garment manufacturing units, complicates skill development. Limited awareness of structured training programs further prevents many workers from benefiting from government-led skilling initiatives.
Government Initiatives to Bridge the Skill Gap
To address these challenges, the Indian government has launched various skilling programs to support workforce development. The Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) remains a flagship initiative, providing industry-relevant training to thousands of youth each year. The Union Budget 2025-26 has allocated ₹5,272 crore to the Ministry of Textiles, marking a 19% increase from the previous year, to enhance skill development, infrastructure, and textile manufacturing innovation.
Samarth Scheme
Launched in 2017, the Samarth scheme is a demand-driven, placement-oriented skilling program. According to the Ministry of Textiles (MoT), over 2.5 lakh individuals have been trained under Samarth, with approximately 70% securing employment in leading textile and apparel firms.
National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS)
The National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS) encourages companies to train apprentices by offering financial incentives. Under this initiative, the government reimburses 25% of the prescribed stipend to the engaged apprentices, ensuring structured on-the-job training for a future-ready workforce.
Transforming Lives Through Skilling: AMHSSC’s Role
The Apparel Made-Ups and Home Furnishing Sector Skill Council (AMHSSC) plays a crucial role in workforce skilling by providing structured training programs. AMHSSC has empowered thousands of individuals, particularly from marginalized communities, by equipping them with essential skills such as stitching, embroidery, garment finishing, soft skills, and financial literacy. These programs enable workers to transition from informal labor to formal employment.
Notably, AMHSSC’s initiatives have promoted gender inclusivity, with nearly 60% of its trained workforce comprising women. Many women have witnessed substantial income growth post-training, enhancing their financial stability and independence.
The Indian textile and apparel industry’s future relies on cultivating a highly skilled workforce. While challenges persist, proactive efforts by the government, industry stakeholders, and skilling bodies like Sector Skill Councils (AMHSSC) are shaping a structured and inclusive workforce development strategy. As skilling initiatives continue to create employment opportunities and uplift livelihoods, they are driving India’s ascent as a global leader in textile and apparel manufacturing.



